Biodiversity finance illustration from ecolife zone (https://www.ecolife.zone/)
18x new research on climate regulation, green millionaires, donations, fintechs, ESG ratings, climate analysts, ESG funds, social funds, smart beta, asset allocation, research risks, green hedge funds, biodiversity, impact funds, proxy voting, sustainable engagement, and timberland investing
Social and ecological research
Non-negative climate regulation? Firms’ Response to Climate Regulations: Empirical Investigations Based on the European Emissions Trading System by Fotios Kalantzis, Salma Khalid, Alexandra Solovyeva, and Marcin Wolski from the International Monetary Fund as of July 15th, 2024 (#13): “Using a novel cross-country dataset … We find that more stringent policies do not have a strong negative impact on the profitability of ETS-regulated or non-ETS firms. While firms report an increase in their input costs during periods of high carbon prices, their reported turnover is also higher. Among ETS-regulated firms which must purchase emission certificates under the EU ETS, tightening of climate policies in periods of high carbon prices results in increased investment, particularly in intangible assets” (abstract).
Greening millionaires? Wealth transfer intentions, family decision-making style and sustainable investing: the case of millionaires by Ylva Baeckström and Jeanette Carlsson Hauff as of June 21st, 2024 (#13): “… little is known about how the wealthy make sustainable investment decisions. Using unique survey data from 402 millionaires … Our results show that funds are more likely to be channeled towards sustainable causes in families that are society-oriented and adopt democratic decision-making styles compared to families whose decision-making style is autocratic and intend for future generations to inherit their wealth” (abstract).
Selfish donations? Donations in the Dark by Ionela Andreicovici, Nava Cohen, Alessandro Ghio, and Luc Paugam as of March 13th, 2024 (#103): “We examine the impact of the 2013 shift from mandatory to voluntary disclosure of corporate philanthropy in the United Kingdom (UK). … we find that, relative to a sample of United States firms, UK firms (i) reduce corporate philanthropy disclosure and (ii) increase corporate philanthropic donations in the voluntary period. … Overall, our results point towards the idea that the shift to voluntary disclosure (i) reduces managerial incentives to transparently report corporate philanthropic activities and (ii) exacerbates managers’ incentives to engage in self-serving corporate donations“ (abstract).
Limited fintech-inclusion: Promise (Un)kept? Fintech and Financial Inclusion by Serhan Cevik from the International Monetary Fund as of July 15th, 2024 (#12): „The ownership of accounts in formal financial institutions increased from 51 percent of the world’s adult population in 2011 to 76 percent in 2021, but there is still significant variation across countries. … While digital lending has a significant negative effect on financial inclusion, digital capital raising is statistically insignificant. … the overall impact of fintech is also statistically insignificant for the full sample, but becomes positive and statistically highly significant in developing countries” (abstract).
ESG investment research (in: Biodiversity finance)
Positive High-ESG effects: The Effects of ESG Ratings on Firms’ Financial Decisions by Sahand Davani as of July 12th, 2024 (#27): “I show that firms with higher ESG ratings (high-ESG firms) have higher ownership by ESG institutional investors, have lower perceived cost of capital, and issue more net equity than net debt compared to similar firms with lower ESG ratings (low-ESG firms). Consistently, I find that high-ESG firms try to maintain their high ESG ratings at the current levels, while the ESG ratings of similar low-ESG firms decline” (abstract).
Analysts climate ignorance: Analysts’ Perspectives on Climate Change: An Examination of Analyst Reports by Jesse Chan as of July 12th, 2024 (#30): “Despite focusing on firms operating in industries most exposed to climate change, I find a minority of analysts (<11%) discuss climate topics in their analyst reports … analysts are concentrating their discussion among electric utilities and other electronic equipment manufacturers, and typically discuss climate change related business opportunities and regulatory issues related to climate change. Climate related discussions, and particularly discussion of regulatory issues, are associated with more pessimistic long-term growth forecasts and revisions, implying analysts expect these issues to affect firms‘ financial performance in the long run” (abstract).
Easy ESG sell? ESG and Mutual Fund Competition? by Ariadna Dumitrescua and Javier Gil-Bazo as of July 12th, 2024 (#37): “Investors have heterogenous preferences for ESG. Not all investors care for sustainability, and among those who do, they value different ESG objectives differently. The model predicts that in equilibrium the market is segmented: neutral investors (those with no preference for ESG) invest only in conventional funds and ESG investors invest only in ESG funds. While competition is fierce in the conventional segment of the market and only the best funds survive, it is relaxed by investors’ ESG preferences in the ESG segment of the market. If the intensity of ESG investors’ preferences is sufficiently high, ESG funds of lower quality will be able to survive“ (p. 18/19).
ESG steering? Smarter Beta Investing: Forget Exclusions, add Steering towards lower Emissions by Heiko Bailer and Jonathan Miller as of July 17th, 2024 (#28): “Steering strategically tilts portfolios towards sustainable factors such as lower emissions … This research investigates the effectiveness of steering compared to exclusion-based strategies. … The analysis, spanning September 2019 to May 2024, reveals that steering maintains or improves risk-adjusted returns compared to exclusions. Additionally, steering portfolios exhibit lower risk and avoid unintended biases toward smaller companies, often observed with exclusions“ (abstract). My comment: The resulting steering strategies appear to have rather limited SDG-revenue alignments. My experience shows attractive risk/return characteristics for strategies using many strict exclusions and demanding ESG- and SDG-Revenue requirements. It would be interesting to compare the results with steering approaches (which may be driven by significant Tech allocations).
Risk reducing ESG: Can Environmental and Social Stocks Weather Market Turbulence? A risk premia analysis by Giovanni Cardillo, Cristian Foroni and Murad Harasheh as of July 23rd, 2024 (#28): “Analyzing all listed firms in the EU and UK and exploiting COVID-19 as an exogenous shock, our findings challenge prior literature by demonstrating that firm sustainability does not necessarily reduce the cost of equity in adverse states of the economy. … Nevertheless, our results indicate that riskier yet more sustainable firms experience a relatively smaller increase in their cost of equity, suggesting a moderating rather than a first-order effect of sustainability. Second, investors positively value firms that reduce CO2 emissions and offer green and more ethical products, as evidenced by lower risk premia assigned to such firms. Lastly, we provide robust evidence that more sustainable firms exhibit less uncertain and higher cash flows during the pandemic than their less sustainable counterparts“ (abstract).
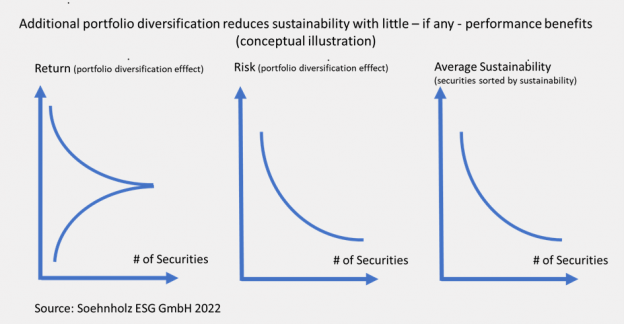
Green optimization limits: Portfolio Alignment and Net Zero Investing by Thierry Roncalli from Amundi as of July 12th, 2024 (#28): “First, the solution is parameter and data sensitive. In particular, we need to be careful in choosing the carbon scope metric … Scope 3 and consumption-based emissions need to be taken into account to align a portfolio with a net-zero scenario. The problem is that we see a lack of data reliability on these indirect emissions today. Similarly, the solution is highly dependent on the green intensity target and the level of self-decarbonization we want to achieve. … The second key finding is that portfolio decarbonization and net-zero construction lead to different solutions. … These results are amplified when we add the transition dimension to the optimization program. … it is quite impossible to achieve net zero alignment without allowing the algorithm to exclude companies (or countries) from the benchmark. … As a result, some key players in the transition, such as energy and utility companies, unfortunately disappear. … The final lesson is that it is easier to implement net zero in bonds than in equities. … there is another important point that is missing from our analysis. This is the issue of engagement. … The reason is that engagement is difficult to model quantitatively” (p. 20-22). My comment: Given the many discretionary decisions for “optimizations”, I usually call them “pseudo-optimizations”.
No green outperformance? Do sustainable companies have better financial performance? Revisiting a seminal study by Andrew King as of July 24th, 2024 (#2180): “Do high-sustainability companies have better financial performance than their low-sustainability counterparts? An extremely influential publication, “The Impact of Corporate Sustainability on Organizational Processes and Performance”, claims that they do. Its 2014 publication preceded a boom in sustainable investing …Yet I report here that I cannot replicate the original study’s methods or results, and I show that a close reading of the original report reveals its evidence is too weak to justify its claims concerning financial performance” (abstract). My comment: It is very important to clearly write, understand and also to replicate scientific studies. But as long as the performance of sustainable investments is similar as the performance of traditional investments, I clearly prefer sustainable investments.
Green hedge funds: Are the Hedges of Funds Green? by Huan Kuang, Bing Liang, Tianyi Qu, and Mila Getmansky Sherman as of April 15th, 2024 (#59): “… we … find that funds with higher green beta not only outperform other funds but also exhibit lower risk. This outperformance is driven by fund managers’ superior investment skill in both green stock picking and green factor timing. Furthermore, we document that investors reward green funds with higher inflows after the 2015 Paris Agreement, but only within high-performance funds. Finally, we show that political beliefs, climate news sentiment, and participation in the United Nations Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI) all influence hedge funds’ exposure to sustainable investing and investor flows” (abstract).
Biodiversity finance and bond risks: Biodiversity Risk in the Corporate Bond Market by Sevgi Soylemezgil and Cihan Uzmanoglu as of July 14th, 2024 (#165): “We investigate how risks associated with biodiversity loss influence borrowing costs in the US corporate bond market. … we find that higher biodiversity risk exposure is associated with higher yield spreads among long-term bonds, indicating biodiversity as a long-run risk. This effect is stronger among riskier firms and firms that mention biodiversity, particularly biodiversity regulation, in their financial statements. … we find that the impact of biodiversity risk on yield spreads is more pronounced when biodiversity-related awareness and regulatory risks rise” (abstract).
Impact investment research
RI market segmentation: Styles of responsible investing: Attributes and performance of different RI fund varieties by Stuart Jarvis from PGIM as of July 2nd, 2024 (#18): “Paris-aligned funds … achieve a low level of portfolio emissions, not just through a combination of significant divestment from sectors but also by selecting companies with low emissions levels. The resulting companies have decarbonised significantly in recent years … Impact funds … have demonstrated willingness to invest in sectors with currently-high emissions … Performance for these funds has been the most challenged in recent years …” (p. 12). My comments see Orientierung im Dschungel der nachhaltigen Fonds | CAPinside
Biodiversity finance overview: Biodiversity Finance: A review and bibliometric analysis by Helena Naffaa and Xinglin Li as of June 26th, 2024 (#31): “Using bibliometric analysis tools, key features of the literature are revealed, influential works are recognized, and major research focuses are identified. This systematic mapping of the field makes contribution to the existing research by providing historical evolution of the literature, identifying the influential works, and current research interests and future research direction“ (abstract).
Empowering small investors? Open Proxy by Caleb N. Griffin as of July 12th, 2024 (#27): “This Article has explored how the world’s largest asset managers have voluntarily implemented programs for “voting choice,” agreeing to pass through a measure of voting authority to selected investors. Unfortunately, the current instantiation of voting choice offers only a narrow set of artificially constrained options, which, in effect, merely transfer a fraction of the Big Three’s voting power to another oligopoly. In order to amplify the choices available to investors, this Article proposes that large asset managers shift from the current closed proxy system to an open proxy system wherein any bona fide proxy advisor could compete for the right to represent investors’ interests. Such a policy change would infuse intermediated voting programs with essential competitive pressure and allow for truly meaningful voting choice” (p. 41).
Depreciation-aligned sustainability: Timing Sustainable Engagement in Real Asset Investments by Bram van der Kroft, Juan Palacios, Roberto Rigobon, and Siqi Zheng as of July 3rd, 2024 (#151): “This paper provides evidence that sustainable engagement improves firms’ sustainable investments only when its timing aligns with the (“real” not “book”) depreciation of their physical assets. … Further, our results appear unexplained by a selection in REITs and are generalized to the US heavy manufacturing industry, heavily relying on real assets. Therefore, this paper argues that sustainable engagement poses an effective tool to improve firms’ sustainable investments when accurately aligned with the depreciation cycles of their physical assets” (p. 35/36).
Other investment research (in: Biodiversity finance)
Attractive timberland: Investing in US Timberland Companies by Jack Clark Francis and Ge Zhang as of June 27th, 2024 (#11): “Over a 20-year sample period it turns out that the US timberland corporations, on average, perform about as well as the highly diversified US stock market index. It is surprising that the timberland companies do not outperform the stock market indexes because, in order to encourage tree planting, the US Congress has almost completely exempted timberland companies from paying federal income taxes. Furthermore, it is scientifically impossible to assess the value of the large amounts of photosynthesis that the timberland companies produce” (abstract). My comment: In my opinion, similar returns clearly speak for the more responsible investments.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Werbehinweis (in: biodiversity finance)
Unterstützen Sie meinen Researchblog, indem Sie in meinen globalen Smallcap-Investmentfonds (SFDR Art. 9) investieren und/oder ihn empfehlen. Der Fonds konzentriert sich auf die Ziele für nachhaltige Entwicklung (SDG: Investment impact) und verwendet separate E-, S- und G-Best-in-Universe-Mindestratings sowie ein breites Aktionärsengagement (Investor impact) bei derzeit 29 von 30 Unternehmen: Vgl. My fund.
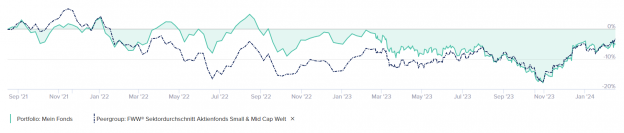
Zur jetzt wieder guten Performance siehe zum Beispiel Fonds-Portfolio: Mein Fonds | CAPinside